Appropriate hand hygiene can minimize
micro – organisms acquired on the hands during daily duties and when there is
contact with blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions and known and unknown
contaminated equipment or surfaces.
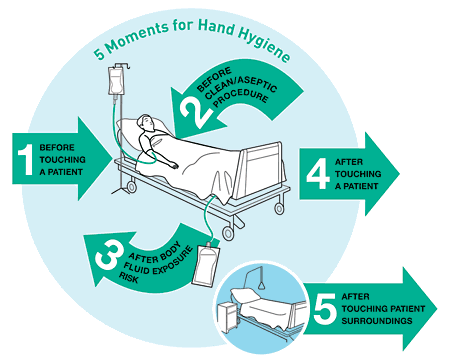
Hands can become contaminated
with infectious agents through contact with a patient, patient surroundings,
the environment, or other health care workers. Cross contamination can occur
from one site to another in the same patient, between health care worker and
patient, between patient or health care worker and the environment, or between
health care workers. Practicing hand hygiene before every episode of patient
contact (including between caring for different patients and between different
care activities for the same patient) and after any activity or contact that
potentially results in hands becoming contaminated (such as removal of gloves)
reduces the risk of cross contamination.
- After handling any Blood, Body Fluids, Secretions, Excretions and Contaminated items between contact with different patients.
- Between contact with different patients
- Between tasks and procedures on the same patient to prevent cross contamination between different body sites
- Immediately after removing gloves
Few Key Factors in effective hand
hygiene and maintaining skin integrity include:
Observed Risk Factors for Poor Adherence to Recommend Hand Hygiene Practises:
Additional perceived barriers to appropriate hand hygiene:
Observed Risk Factors for Poor Adherence to Recommend Hand Hygiene Practises:
- We need to monitor doctor Status (rather than nurse)
- We need to monitor nursing assistant Status (rather than nurse)
- We need to monitor all ICU Staff Status
- We need to monitor all ICU & O.T Staff Gloves Wearing Status
- We need to monitor all Activities with High Risk of Cross Transmission
Observed Self Reported Factors for Poor Adherence to Recommend Hand Hygiene Practises:
- Hand washing agents cause irritation and dryness
- Sinks are inconveniently located / shortage of sinks
- Lack of soap and paper towels
- Often too busy / Insufficient time
- Under staffing
- Over Crowding
- Patient needs take priority
- Hand hygiene interferes with healthcare worker relationship with patients
- Feel Low risk of acquiring infection from patients
- Wearing of gloves / beliefs that gloves use obviates the need for hand hygiene
- Lack of Knowledge about protocols
- No role model from colleagues or Supervisor
- Lack of scientific information definite impact of approved hand hygiene on HAI rates
- Lack of active participation in hand hygiene promotion at individual or Hospital level
- Lack of role model for hand hygiene
- Lack of Hospital priority for hand hygiene
- Lack of administrative sanction of non compliers / Rewarding compliers
- Lack of Institutional safety climate

Written by:
Dr. Praveen Bajpai
Director of Ingenious Healthcare Consultants Pvt. Ltd.
Founder of Skill Sathi
MBA in Hospital administration, PG Diploma in Quality Accreditation, PG Diploma in Medico Legal System, M. Phil in Hospital Mgmt. from BITS Pilani, P.hD in Management, Certified NABH Auditor, Certified NABL Auditor, Certified Auditor for Clinical Audits, Green Belt in Six Sigma, Certified in Hospital Infection Control Practices, Certified trainer for International Patient Safety Goals, Certified Auditor for JCI 7th Edition Standards
www.skillsathi.in



















Comments
Post a Comment